Proxy Error Guide: Causes, Common Codes & Solutions
In today's digital world, proxies are widely used for a variety of purposes, from enhancing security to enabling access to geo-restricted content. However, despite their numerous benefits, proxy errors can be frustrating and disruptive.
Understanding what causes proxy errors, how to diagnose them, and how to resolve them is essential for anyone using proxies in their network environment.
In this article, we will explore the causes of proxy errors, dive into common error codes, and offer practical solutions for overcoming them.
What is a Proxy Error and Common Causes
A proxy error occurs when a request made through a proxy server fails to complete as expected. It could be due to an issue with the proxy server itself, the destination server, or an intermediate network element. Proxy errors are often encountered in various contexts, particularly when performing web scraping, SEO analysis, automation tasks, or using proxy services.

Common Causes of Proxy Errors
- IP Blocking/Blocking by Target Server: Websites often block proxy IPs to prevent misuse, especially for scraping or other suspicious activities. This leads to errors like 403 Forbidden or 502 Bad Gateway.
- Incorrect DNS Settings: Improper DNS configurations can result in the inability to resolve the IP address of the target website, leading to a connection failure.
- Network Issues: Problems like high latency, packet loss, or intermittent connectivity can lead to timeout errors, such as the 504 Gateway Timeout.
- Server Failures: If the proxy server is down, or the target server is unreachable (due to downtime, maintenance, or overload), requests cannot be processed, triggering various proxy errors.
- Authentication Failures: Some proxies require authentication. If credentials are incorrect or expired, errors like 401 Unauthorized or 407 Proxy Authentication Required can occur.
- Firewall Configuration Errors: Firewalls may block proxy traffic due to incorrect rules, resulting in connection failure or timeouts.
Proxy Error Codes: HTTP Status Code Categories
HTTP status codes provide insight into the type of error that occurred. They are divided into five categories, with each category indicating a different nature of the response. Below is a breakdown of these categories, followed by a more detailed analysis of 3xx, 4xx, and 5xx errors, common in proxy-related issues.
| Code Range | Description | Common Errors in Proxy Context |
|---|---|---|
| 1xx | Informational | No proxy errors in this range. |
| 2xx | Success | 200 OK (Proxy succeeds) |
| 3xx | Redirection | 301 Moved Permanently, 302 Found |
| 4xx | Client Error | 403 Forbidden, 407 Proxy Authentication Required |
| 5xx | Server Error | 502 Bad Gateway, 504 Gateway Timeout |
3xx Errors: Redirection
Redirection errors occur when the requested resource has moved or needs to be accessed from a new location. Proxy servers must handle these redirects properly to continue processing the request.
- ⚠️301 Moved Permanently: The resource has permanently moved to a new URL. The proxy must follow the new URL.
🔧 Fix: Proxy should automatically follow the redirection to the new location. - ⚠️302 Found: The resource has temporarily moved. The proxy must handle this temporary redirection and follow the new URL.
🔧 Fix: Proxy should process the redirection but remember that this is temporary. - ⚠️304 Not Modified: The requested resource has not been modified since the last request, so the proxy can use a cached version.
🔧 Fix: Use the cached version of the resource if available. No need to fetch again. - ⚠️307 Temporary Redirect: The resource is temporarily moved, and the proxy should follow the new URL using the same HTTP method.
🔧 Fix: Proxy must respect the temporary redirect and handle it with the same HTTP method.
4xx Errors: Client Errors
Client errors generally point to issues with the proxy settings, the request sent by the proxy, or authentication failures.
- ⚠️400 Bad Request: The server cannot process the request due to malformed syntax.
🔧 Fix: Check the proxy configuration and ensure the request is correctly formatted. Verify the target URL and headers. - ⚠️401 Unauthorized: The request requires authentication, but the proxy or client hasn’t provided valid credentials.
🔧 Fix: Ensure the correct authentication credentials are provided for the proxy. - ⚠️403 Forbidden: The proxy’s IP address is blocked by the server, or the server refuses to process the request for security reasons.
🔧 Fix: Use a different proxy IP, switch to residential proxies, or contact the website admin for whitelisting. - ⚠️404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found on the server.
🔧 Fix: Verify the requested URL and ensure it is correct. If the URL is outdated or incorrect, update it. - ⚠️407 Proxy Authentication Required: The proxy server requires authentication, but the client hasn't provided the correct credentials.
🔧 Fix: Ensure proper proxy authentication credentials are set up and configured. - ⚠️408 Request Timeout: The server timed out waiting for the request from the proxy.
🔧 Fix: Check the network connection and ensure the proxy server is responsive. Retry the request after a short period. - ⚠️429 Too Many Requests: The proxy server has sent too many requests in a short period and is being rate-limited.
🔧 Fix: Reduce the frequency of requests, implement request throttling, or use rotating IPs to distribute the load. - ⚠️499 Client Closed Request: The client closed the connection before the server could respond.
🔧 Fix: Investigate the client-side application to prevent it from prematurely closing the connection.
5xx Errors: Server Errors
Server errors typically occur when the proxy server is unable to retrieve a valid response from the destination server. This could be due to server overloads, network issues, or misconfigurations.
- ⚠️500 Internal Server Error: The server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request.
🔧 Fix: Check the target server’s logs for any issues. Retry the request after some time, as this is often a temporary issue. - ⚠️501 Not Implemented: The server does not recognize the request method or lacks the capability to fulfill the request.
🔧 Fix: Ensure that the HTTP method used in the request is supported by the target server. Consider adjusting the request. - ⚠️502 Bad Gateway: The proxy server received an invalid response from the upstream server.
🔧 Fix: Check if the destination server is available, clear the proxy cache, or retry the request later. If the problem persists, verify server health or reach out to the upstream provider. - ⚠️503 Service Unavailable: The server is temporarily unavailable, usually due to overload or maintenance.
🔧 Fix: Retry the request after a few minutes or hours. If possible, check the server's status or schedule maintenance windows. - ⚠️504 Gateway Timeout: The proxy couldn’t reach the destination server within the timeout period.
🔧 Fix: Ensure the target server is reachable, check network latency, and consider reducing request frequency to avoid timeouts. - ⚠️505 HTTP Version Not Supported: The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request.
🔧 Fix: Ensure that the proxy is using an HTTP version compatible with the destination server. If necessary, downgrade the protocol version in the request.
How to Overcome Proxy Errors: More Tips
Here are several strategies and tips for overcoming proxy errors:
1. Check Proxy Settings
Ensure that the proxy settings (IP, port, and protocol) are correctly configured. Misconfiguration is a common cause of proxy errors.
2. Refresh the Page
Sometimes, a simple page refresh can resolve proxy errors, especially if the error was caused by a transient issue, such as a temporary network glitch.
3. Clear Browser Cache and Reset Proxy Settings
In some cases, your browser's cache may be outdated and cause proxy errors. Clearing your cache can help resolve issues where cached information is conflicting with the proxy server’s request.
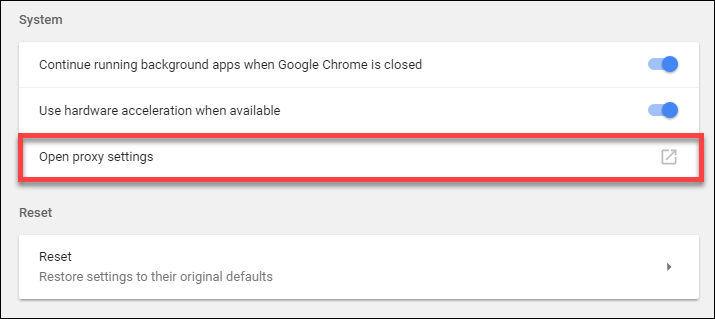
If you're encountering persistent proxy errors, you might also need to reset proxy settings in Chrome. Here's how to do it:
Open Chrome > Settings > Advanced > System > Open Proxy Settings
In the Internet Properties window, go to the Connections tab.
Under LAN Settings, uncheck "Use a proxy server" if it's enabled.
4. Adjust Request Frequency
If you are making a large number of requests in a short period, proxies may get blocked. Try reducing the frequency of requests to prevent overwhelming the proxy server or target website.
5. Use Residential Proxies and Rotate IP Addresses
Residential proxies are less likely to be blocked by target websites since they appear as regular users. Implementing IP rotation can also help bypass temporary IP bans and prevent the detection of automated actions.
Final Thoughts
Proxy errors can be disruptive and frustrating, especially when they impede your access to essential resources. By understanding the common causes, knowing how to diagnose errors, and employing practical solutions, you can significantly reduce the frequency and impact of proxy errors.
Always ensure your proxy settings are optimized, and consider using residential proxies for a more reliable and secure browsing experience. Proxies are valuable tools, but understanding how to troubleshoot and resolve errors is essential for maintaining smooth and efficient operations.