Vous est-il déjà arrivé de vous connecter au réseau WiFi public d'un hôtel, d'une école ou d'un bureau et de constater que certains sites web ne se chargeaient pas ? Ou avez-vous remarqué une invite vous demandant de configurer un "proxy" avant de pouvoir accéder à l'internet ? Ces situations sont plus fréquentes que la plupart des gens ne le pensent, et elles sont généralement liées à un proxy WiFi.
Les réseaux WiFi étant de plus en plus étroitement gérés pour des raisons de sécurité, de confidentialité et de contrôle du contenu, les proxys WiFi sont de plus en plus utilisés en coulisses. Pour comprendre pourquoi ils sont importants et quand vous pourriez en avoir besoin, il est utile de comprendre d'abord ce qu'est un proxy WiFi.
Qu'est-ce qu'un proxy WiFi ?
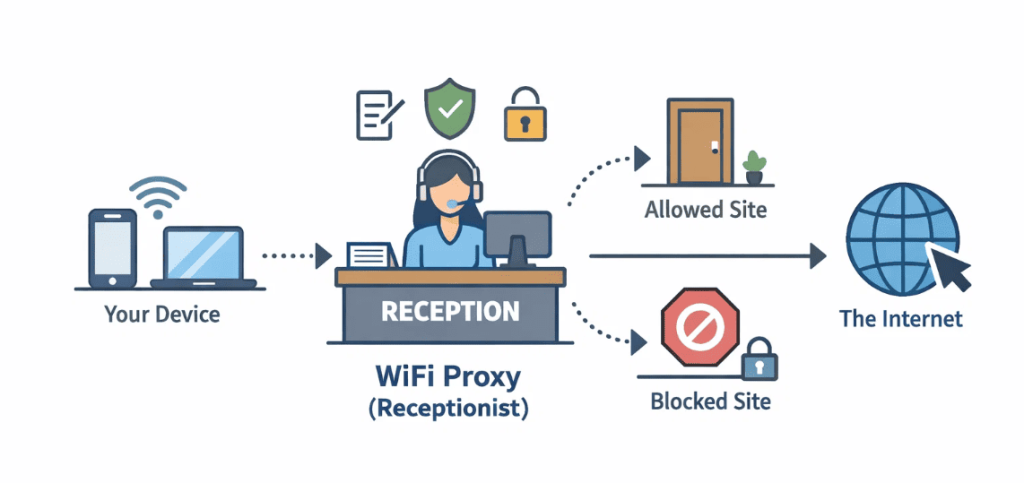
D'un point de vue technique, un serveur proxy WiFi est un serveur intermédiaire qui s'interpose entre votre appareil et l'internet lorsque vous vous connectez via un réseau WiFi. Au lieu que votre appareil communique directement avec un site web, votre trafic est d'abord acheminé par le serveur proxy. Le proxy transmet ensuite votre demande au site web de destination et vous renvoie la réponse.
Cette configuration permet de renforcer la sécurité, de protéger la vie privée en masquant votre adresse IP, de filtrer le contenu et parfois d'améliorer les performances grâce à la mise en cache. Votre appareil ne se connecte jamais directement au site web - il communique avec le proxy, qui agit en votre nom. Ceci est particulièrement important sur les réseaux WiFi publics non sécurisés.
Pour simplifier, considérez un proxy WiFi comme un réceptionniste dans un immeuble de bureaux. Au lieu que les visiteurs entrent directement dans chaque bureau (votre appareil accédant directement à l'internet), ils s'enregistrent d'abord à la réception. La réceptionniste décide où les envoyer, tient un registre des visites et empêche tout accès non autorisé.
Proxy WiFi vs VPN
Bien que les proxys WiFi et les VPN soient souvent mentionnés ensemble, ils ont des objectifs différents. Le tableau ci-dessous met en évidence les principales différences :
| Fonctionnalité | Proxy WiFi | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Couverture du trafic | Au niveau de l'application ou du navigateur | Tout le trafic de l'appareil |
| Cryptage | Limitée ou nulle | Cryptage complet |
| Masquage IP | Oui | Oui |
| Vitesse et flexibilité | Plus rapide, plus souple | Légèrement plus lent en raison du cryptage |
| Meilleur cas d'utilisation | Filtrage, contrôle d'accès, automatisation | Vie privée et sécurité sur les réseaux publics |
En résumé, les proxys se concentrent sur l'acheminement et le contrôle du trafic, tandis que les VPN se concentrent sur le cryptage et la protection complète des appareils.
Comment fonctionne un proxy WiFi ?
Maintenant que nous avons présenté le concept de proxy WiFi, examinons de plus près son fonctionnement. Le processus est assez simple et se déroule en coulisses lorsque vous accédez à un site web par l'intermédiaire d'un proxy.
- Demande envoyée au serveur mandataire: Lorsque vous essayez de visiter un site web, au lieu d'envoyer la demande directement au site web, votre appareil l'envoie d'abord au serveur proxy.
- Le mandataire transmet la demande: Le serveur proxy prend alors votre demande et la transmet au site web réel, mais au lieu d'utiliser l'adresse IP de votre appareil, il utilise sa propre adresse IP pour effectuer la demande.
- Retour de la réponse au mandataire: Une fois que le site web a traité votre demande, il renvoie la réponse au serveur proxy, et non directement à votre appareil.
- Le proxy envoie des données à votre appareil: Enfin, le serveur proxy renvoie les données (telles que le contenu d'un site web) à votre appareil, achevant ainsi le cycle.
Ce processus permet non seulement de dissimuler votre véritable adresse IP, mais aussi de contrôler et de sécuriser le trafic. C'est pourquoi de nombreuses organisations, comme les écoles et les entreprises, ont besoin de proxys WiFi. Ils utilisent les proxys pour contrôler et restreindre l'accès à certains sites web, réduire les risques de sécurité et garantir le respect des politiques d'utilisation de l'internet.
En fait, certains réseaux WiFi n'autorisent pas l'accès à l'internet si une adresse proxy n'est pas configurée, ce qui garantit que tout le trafic passe par une passerelle contrôlée pour une meilleure surveillance et une meilleure sécurité.
Cas d'utilisation et avantages des serveurs mandataires WiFi
Les proxys WiFi sont incroyablement polyvalents et répondent à un large éventail d'objectifs dans les environnements personnels et professionnels. Voici quelques-unes des applications les plus courantes et les avantages qu'elles procurent :
1. Contourner les restrictions WiFi
Les proxys WiFi peuvent aider à contourner les restrictions imposées par des réseaux tels que ceux des écoles, des bureaux ou des hôtels, qui bloquent souvent certains sites web ou services en ligne.
📌 Benefit :
Avec un proxy en place, les utilisateurs peuvent accéder librement au contenu bloqué, que ce soit pour le travail, l'étude ou l'usage personnel, sans avoir à s'inquiéter des restrictions du réseau.
2. Améliorer la protection de la vie privée sur les réseaux WiFi publics
Lorsque vous vous connectez à des réseaux WiFi publics, comme ceux des cafés, des aéroports ou des centres commerciaux, votre adresse IP et vos activités en ligne peuvent être facilement suivies et surveillées. Un proxy WiFi dissimule votre véritable IP, ce qui contribue à protéger votre vie privée.
📌 Benefit :
L'utilisation d'un proxy empêche que votre IP soit exposée, vous protégeant ainsi d'une éventuelle surveillance et réduisant le risque d'interception des données lorsque vous naviguez sur des réseaux non fiables.

3. Accès au contenu et tests géographiques
Les serveurs mandataires peuvent être utilisés pour tester la manière dont le contenu est affiché dans différents pays ou régions. En utilisant un serveur proxy dans un autre endroit, vous pouvez simuler la navigation à partir de ce pays pour voir le contenu géo-restreint.
📌 Benefit :
Cela permet aux spécialistes du marketing, aux chercheurs et aux développeurs de s'assurer que leur contenu s'affiche correctement dans différentes régions ou de tester des campagnes ciblées pour différents publics.
4. Gestion des comptes et automatisation
Gérer plusieurs comptes sur des plateformes de médias sociaux, des sites de commerce électronique ou d'autres services en ligne peut s'avérer difficile. Avec un proxy WiFi, vous pouvez gérer de nombreux comptes sans déclencher d'alertes de sécurité ni risquer d'être banni en raison d'une activité suspecte.
📌 Benefit :
Cette fonction est particulièrement utile pour automatiser des tâches telles que publier, aimer ou suivre/désappliquer plusieurs comptes, ce qui permet une gestion efficace et à grande échelle des comptes sans enfreindre les règles de la plateforme.
5. Filtrage et surveillance du trafic (utilisation en entreprise)
Les grandes entreprises utilisent souvent des proxys pour acheminer l'ensemble du trafic internet via une passerelle unique et contrôlée, minimisant ainsi les risques de sécurité associés à l'accès direct à l'internet sur tous les appareils.
📌 Benefit :
L'utilisation d'un serveur proxy pour le filtrage et la surveillance permet à l'organisation de suivre l'ensemble du trafic entrant et sortant, d'identifier les intrusions ou les cyberattaques potentielles et d'appliquer efficacement les politiques d'utilisation de l'internet. La surveillance est également centralisée, ce qui facilite la détection de toute activité non autorisée ou suspecte.
6. Navigation anonyme et accès à des contenus restreints (usage personnel)
Les proxys sont largement utilisés pour la navigation anonyme ou l'accès à des contenus restreints par la localisation géographique (par exemple, des vidéos ou des sites web verrouillés par région, etc.) Bien que les VPN offrent souvent un meilleur cryptage, les proxys peuvent toujours être utiles à ces fins.
📌 Benefit :
Pour un usage personnel, les proxys offrent un moyen rapide et facile d'accéder au contenu sans révéler votre identité réelle ou votre emplacement, ce qui est idéal pour contourner les restrictions géographiques ou maintenir un certain niveau d'anonymat lors de la navigation.
Types courants de mandataires WiFi
Les mandataires ne sont pas tous les mêmes et le choix du bon type de mandataire est important.
Ces proxys sont utilisés par plusieurs utilisateurs à la fois. Ils sont abordables mais peuvent souffrir de vitesses plus lentes et de taux de blocage plus élevés.
Procurations publiques
Gratuits et largement disponibles, les proxys publics sont généralement peu fiables et risqués en raison d'une sécurité insuffisante et d'abus importants.
Procurations résidentielles
Les proxys résidentiels utilisent des adresses IP attribuées par de véritables fournisseurs d'accès à l'internet, ce qui les fait passer pour des connexions domestiques normales. Les sites web leur font beaucoup plus confiance et ils fonctionnent bien sur les réseaux WiFi restrictifs.
👍 Recommandé : Des fournisseurs comme OkeyProxy offrent un accès à plus de 150 millions de IP résidentielles sur plus de 200 sites, ce qui les rend idéaux pour l'utilisation stable de proxy WiFi, l'automatisation et l'accès basé sur la géographie avec un risque de détection réduit.
Proxies mobiles
Ces proxys acheminent le trafic via les IP des opérateurs mobiles. Ils offrent d'excellents niveaux de confiance mais sont généralement plus chers.
Procurations tournantes
Les proxys rotatifs changent automatiquement d'adresse IP à intervalles déterminés, ce qui est utile pour les tâches à grande échelle ou les scénarios de "scraping".
Comment configurer un proxy WiFi (étape par étape)
La mise en place d'un proxy WiFi peut sembler technique, mais en pratique, cela ne prend que quelques minutes. Vous trouverez ci-dessous un guide clair, étape par étape, pour les appareils les plus courants. Les noms des menus peuvent varier légèrement en fonction de la version ou de la marque du système, mais le processus général est le même.
📱 Sur Android
Android vous permet de configurer un proxy directement pour chaque réseau WiFi, ce qui le rend flexible pour une utilisation personnelle ou professionnelle.
Étape 1 : Ouvrir les paramètres WiFi
Aller à Paramètres → WiFi et connectez-vous au réseau WiFi que vous souhaitez utiliser, ou appuyez sur le réseau auquel vous êtes déjà connecté.
Étape 2 : Modifier le réseau
Appuyez sur le réseau WiFi et maintenez-le enfoncé, puis sélectionnez Modifier le réseau ou Paramètres avancés (la formulation peut varier selon l'appareil).
Étape 3 : Configurer le proxy
Trouvez l'option Proxy et mettez-la sur Manuel.
Saisissez le nom d'hôte du proxy (adresse du serveur) et le port fournis par votre service de proxy.
Si nécessaire, saisissez également votre nom d'utilisateur et votre mot de passe.
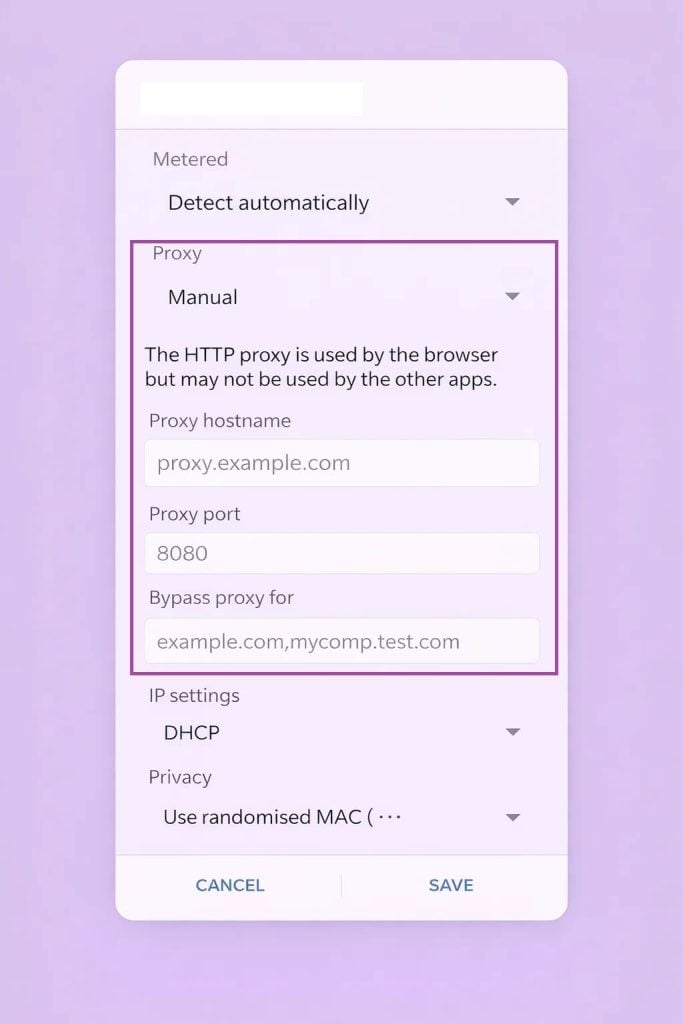
Étape 4 : Sauvegarde et reconnexion
Enregistrez les paramètres et reconnectez-vous au réseau WiFi pour appliquer les modifications.
📱 Sur iOS (iPhone et iPad)
Sur iOS, les paramètres du proxy sont également configurés par réseau WiFi et sont très simples.
Étape 1 : Ouvrir les paramètres WiFi
Aller à Paramètres → WiFi et assurez-vous que vous êtes connecté au réseau souhaité.
Étape 2 : Accéder aux options du proxy
Appuyez sur la touche Icône ⓘ (info) à côté du réseau WiFi connecté.
Faites défiler vers le bas jusqu'à Proxy HTTP et sélectionnez Manuel.
Étape 3 : Entrer les détails de la procuration
Remplissez les informations relatives au serveur et au port fournies par votre fournisseur de proxy.
Si l'authentification est requise, entrez votre nom d'utilisateur et votre mot de passe.
Étape 4 : Enregistrer et commencer à naviguer
Une fois enregistré, le proxy prendra effet immédiatement pour ce réseau WiFi.
💻 Sous Windows
Windows vous permet de configurer un proxy à l'échelle du système, qui s'applique à la plupart des applications et des navigateurs.
Étape 1 : Ouvrir les paramètres du réseau
Aller à Paramètres → Réseau et Internet.
Étape 2 : Activer la configuration manuelle du proxy
Cliquez sur Proxy dans le menu de gauche, puis activez Utiliser un serveur proxy.
Étape 3 : Saisir les informations relatives au serveur
Saisissez l'adresse et le port du proxy fournis par votre service de proxy.
Enregistrez les modifications.
Étape 4 : Tester la connexion
Ouvrez votre navigateur et visitez un site web pour confirmer que le proxy fonctionne correctement.
💻 Sur macOS
La mise en place d'un proxy WiFi sur macOS est simple, et le processus reste le même pour la plupart des versions de macOS.
Étape 1 : Accéder aux paramètres du réseau
Aller à Paramètres du système → Réseau et sélectionnez le réseau WiFi auquel vous êtes actuellement connecté.
Cliquez sur Détails (ou Avancéselon la version de macOS que vous utilisez).
Étape 2 : Configurer le proxy
Dans la fenêtre des paramètres, naviguez jusqu'à l'onglet Proxies tabulation.
Activez le type de proxy dont vous avez besoin - HTTP, HTTPS ou SOCKS, selon les spécifications de votre fournisseur de proxy.
Étape 3 : Entrer les détails du serveur
Saisissez le nom d'hôte (adresse du serveur) et le numéro de port fournis par votre fournisseur de proxy.
Étape 4 : Enregistrer et appliquer
Cliquez sur OKpuis Appliquer pour activer le proxy sur votre réseau WiFi.
En suivant ces étapes, vous pouvez rapidement mettre en place un proxy WiFi sur n'importe quelle plateforme majeure. Si vous changez fréquemment de réseau ou gérez plusieurs IP, l'utilisation d'une application proxy dédiée ou d'un outil proxy avancé peut rendre le processus encore plus facile et plus stable.
Comment vérifier si votre WiFi utilise un proxy
Après avoir configuré un proxy WiFi, ou lorsque vous utilisez des réseaux publics ou d'entreprise, il est important de vérifier si votre connexion passe effectivement par un proxy. Il existe quelques moyens simples de vérifier.
1. Vérifiez les paramètres du réseau WiFi sur votre appareil
La méthode la plus directe consiste à revoir votre configuration WiFi actuelle :
Android / iOS :
Allez dans les paramètres WiFi, appuyez sur votre réseau connecté et recherchez Proxy / HTTP Proxy.
S'il est réglé sur Manuel et qu'une adresse de serveur et un port sont présents, votre WiFi utilise un proxy.
Fenêtres :
Naviguez vers Paramètres → Réseau et Internet → Proxy.
Si l'option "Utiliser un serveur proxy" est activée, le trafic peut être acheminé via un proxy.
macOS :
Allez dans Paramètres du système → Réseau → WiFi → Détails → Proxies.
Tout type de proxy coché (HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS) indique l'utilisation d'un proxy.
📌 Bénéfice: Cette méthode vous permet d'obtenir une confirmation claire au niveau du système sans avoir recours à des outils tiers.
2. Comparez votre adresse IP avant et après la connexion
Vous pouvez également vérifier l'utilisation du proxy en consultant votre adresse IP publique :
- Déconnectez-vous du WiFi et notez votre adresse IP.
- Reconnectez-vous au réseau WiFi (avec le proxy activé).
- Vérifiez à nouveau votre adresse IP.
Si l'adresse IP a été remplacée par une adresse fournie par le serveur proxy, ce dernier est actif.
📌 Bénéfice: Confirme si votre IP réelle est masquée par le proxy.
3. Rechercher des invites de connexion ou d'authentification
Certains serveurs mandataires WiFi, en particulier dans les bureaux, les écoles ou les hôtels, exigent une authentification.
Si votre navigateur vous demande un nom d'utilisateur et un mot de passe avant d'autoriser l'accès à l'internet, cela indique clairement que le réseau utilise un serveur proxy.
📌 Bénéfice: Identifie rapidement les réseaux basés sur un proxy sans avoir à fouiller dans les paramètres.
4. Tester les sites web qui détectent les proxies
Certains sites web et outils de réseau peuvent détecter des en-têtes ou des comportements de routage liés au proxy.
Si un site signale que votre connexion provient d'un proxy ou affiche des en-têtes de réseau inhabituels, il est probable que votre trafic WiFi soit proxié.
📌 Bénéfice: Permet de confirmer l'utilisation du proxy lorsque les paramètres de l'appareil sont verrouillés ou restreints.
Il est essentiel de savoir si votre réseau WiFi utilise un proxy pour résoudre les problèmes de connectivité, améliorer la confidentialité ou optimiser les performances, en particulier sur les réseaux partagés ou restreints.
Conclusion
Un proxy WiFi n'est pas un type particulier de proxy : c'est un moyen pratique d'acheminer le trafic internet via un intermédiaire contrôlé lors de l'utilisation de réseaux WiFi. Qu'il s'agisse de contourner des restrictions, d'améliorer la confidentialité, de gérer des comptes ou de sécuriser des réseaux d'entreprise, les proxy WiFi jouent un rôle essentiel dans la connectivité moderne.
Comprendre leur fonctionnement et choisir des types de proxy fiables, comme les IP résidentielles ou mobiles, peut rendre votre expérience WiFi plus sûre, plus flexible et plus fiable.






![Proxies anonymes : Ce qu'ils sont et comment les utiliser [Guide] proxies anonymes](https://www.okeyproxy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/anonymous-proxies-500x278.png)

