Imagine for a moment that you are tasked with teaching a visitor from a far-off galaxy what an “apple” is. This alien is incredibly intelligent, but they don’t speak a word of English—or any human language, for that matter. However, they have a superpower: they are absolute geniuses with numbers. They can calculate complex trajectories in their head in a heartbeat, but the word “red” or “sweet” means nothing to them.
To explain an apple, you decide to use a coordinate system. You tell the alien: “On the Sweetness Axis, this object is a 7. On the Crunchiness Axis, it’s an 8. On the Color Spectrum, it sits at coordinate 650 (Red).”
Suddenly, the alien “gets” it. They don’t know the word apple, but they understand its mathematical position relative to a “lemon” or a “rock.” This is the essence of the meaning of mapping a text for an AI. It is the process of taking our messy, emotional, and complex human language and translating it into a “map” of numbers (vectors) that a computer can calculate.
What Does “Mapping a Text” Mean in Simple Terms?
When we talk about the meaning of mapping a text for an AI, we are describing the transformation of language into a spatial “map.”
In our human brains, a word like “Cat” triggers an image of fur, whiskers, and perhaps a memory of a pet. In an AI’s “brain,” there are no images—only a multi-dimensional space. Think of it like a massive, 3D (or even 10,000-dimensional) room. Every word in existence has a specific seat in that room.
The key to this map is proximity. In a well-mapped AI system:
- “Cat” and “Dog” are sitting right next to each other because they are both pets and animals.
- “Cat” and “Kitten” are practically in the same seat.
- “Cat” and “Smartphone” are on opposite sides of the room because they have almost nothing in common.
Human Understanding vs. AI Mapping
| Dimension | Human Understanding (Text) | AI Mapping (Vectors / Math) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Unit | Words, phrases, and feelings | Lists of numbers (e.g., [0.12, -0.5, 0.8]) |
| Logic | “An apple is a fruit.” | “Apple” and “Fruit” have high mathematical similarity |
| Processing | Reading, empathy, and context | Matrix multiplication and probability |
| Goal | To communicate or feel | To predict the next logical coordinate |
What Is a “Text Map” Made Of? (Common Mapping Forms)
“Mapping” isn’t just one single action; it’s a toolkit. Depending on what the AI needs to do, the “map” might look different. Here are the five most common ways AI maps our text:
① Tokenization (Text Splitting)
This is the “Lego” stage. Before an AI can map a sentence, it breaks it into smaller pieces called tokens.
Esempio: “I love sunshine” becomes [“I”, “love”, “sunshine”].
② Embedding (Text to Numbers)
This is the most famous form of mapping. It assigns every token a set of coordinates in that massive “room” we talked about.
Esempio: The word “King” might be mapped to a point in space. If you subtract the “Man” coordinates from “King” and add “Woman” coordinates, the AI’s map will literally point it toward the coordinates for “Queen.”
③ Tagging (Text to Labels)
Here, the AI maps words to their grammatical or structural roles.
Esempio: In the sentence “Apple is hiring,” the AI maps “Apple” to the label [Organization] rather than [Fruit].
④ Information Extraction (Text to Structure)
This maps messy paragraphs into neat tables.
Esempio: Mapping a flight confirmation email into a structured map of: Date: Oct 10, Destination: NYC, Gate: B2.
⑤ Feature Mapping (Text to Patterns)
The AI maps text to specific “vibes” or styles.
Esempio: Example: It maps a long email to a “Formal” pattern or a “Sarcastic” pattern.
How Is This “Map” Actually Created? (Step-by-Step)
Creating a text map is like building a GPS system for human thought. It happens in three sophisticated steps:
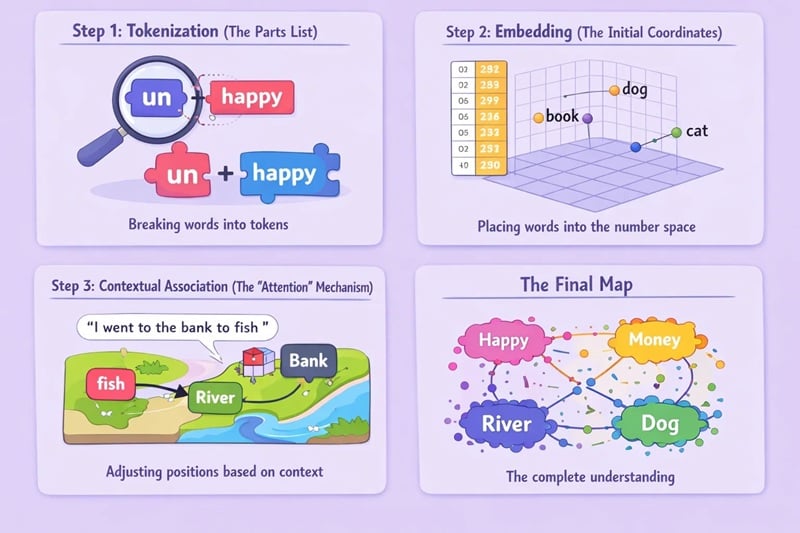
Step 1: Tokenization (The Parts List)
The AI first deconstructs your sentence. It doesn’t just look at words; it looks at prefixes and suffixes. For example, “unhappy” might be split into un and happy. This helps the AI understand that “un” usually means “the opposite of” wherever it appears on the map.
Step 2: Embedding (The Initial Coordinates)
The AI looks up each token in its “dictionary.” But this isn’t a normal dictionary; it’s a giant table of numbers. Each word gets an initial position. However, these positions are static—they don’t know who their neighbors are yet.
Step 3: Contextual Association (The “Attention” Mechanism)
This is the “magic” of modern AI like ChatGPT. It uses something called Attention. Think of it like a GPS that updates in real-time.
- If the text says: “I went to the bank to fish,” the word “fish” sends a signal to “bank.”
- The AI then shifts the coordinates of “bank” away from “money” and toward “river.”
- This dynamic mapping ensures the AI “understands” the specific meaning of the word in that specific sentence.
A Simple Example: Mapping Text Step-by-Step
Let’s see how an AI maps the sentence: “The bat flew over the field.”
1️⃣ Tokenizzazione: [The, bat, flew, over, the, field]
2️⃣ Initial Mapping: “Bat” could be a baseball bat or an animal. Its coordinate is currently in the “middle.”
3️⃣ Contextual Mapping:
- The AI sees the word “flew.”
- “Flew” is a neighbor of “wings,” “sky,” and “birds.”
- The AI applies Attention: It pulls the coordinate for “bat” closer to the “animal/mammal” section of the map and further away from the “sports equipment” section.
4️⃣ Final Result: The AI now has a mathematical map where “bat” is located near “nocturnal creatures.”
Why Do We Bother Mapping Text?
Mapping sounds like a lot of mathematical heavy lifting. Why not just let the AI read the words like we do? Because mapping allows the AI to perform “miracles” that simple keyword matching cannot:
- Semantic Search: If you search for “infant apparel,” a mapped AI knows to show you “baby clothes.” Even though the words are different, their positions on the “map” are almost identical.
- Sentiment Analysis: AI can map the “tone” of a review. It can see if a customer is being genuinely happy or using “sarcastic coordinates” to complain about a product.
- Universal Translation: This is the most beautiful use. AI maps “Apple” (English) and “Pingguo” (Chinese) to the exact same coordinate in its conceptual map. To the AI, it’s the same point; it just has two different names in human languages.
What Is Required to Build These Maps?
To build a map of the entire human language, an AI needs to “read” almost everything ever written—billions of webpages, books, and articles. This is called “training data.”
However, gathering this data isn’t always easy. Many researchers and developers face a significant hurdle: Data Access.
To make an AI’s “map” complete and unbiased, researchers must gather text from all over the world. However, many websites have restrictions or regional blocks that prevent easy access to this data. This is where reliable tools like OkeyProxy come into play. By using deleghe residenziali, AI developers can access diverse, global text data without being blocked by servers, ensuring their AI “map” is as accurate and inclusive as possible.
Common Misconceptions: Does the AI “Understand” Me?
It is easy to get carried away and think the AI is truly “thinking.” We must be candid: an AI doesn’t “know” what a mother’s love feels like or what a strawberry tastes like. It only knows that those words have specific mathematical relationships to other words.
- ❌ Mapping ≠ Translation: It’s the process that enables translation.
- ❌ Mapping ≠ Labeling: Labeling is just one small type of map.
- ❌ Mapping ≠ Consciousness: The AI isn’t “thinking”; it is calculating the shortest distance between two points in a massive cloud of data.
- ✅ Mapping = Mathematical Representation: It is the bridge between human poetry and computer logic.
Is Mapping a Text the Same as Training an AI?
This is a frequent point of confusion. Think of it this way: Training is the long, expensive process of building the “map room” and teaching the AI where all the furniture goes. Mapping is what the AI does every time you type a prompt into the box.
| Caratteristica | Training an AI | Mapping a Text |
|---|---|---|
| When it happens? | Months before the AI is released | Every time you hit “Enter” |
| Does it change the AI? | Yes, it creates the AI’s “brain” | No, it just uses the existing “brain” |
| Resource Cost | Millions of dollars in electricity and chips | Fractions of a cent |
| Goal | Learning the relationships between words | Placing a specific sentence on the map |
Conclusion: Mapping is the Foundation of AI Intelligence
Without text mapping, AI would be a blind machine, seeing nothing but a jumble of letters and symbols. Mapping is what gives AI its “vision.” It transforms our stories, our questions, and our data into a logical landscape where the computer can finally meet us halfway.
💡 Appendix: A Layperson’s Glossary of AI Text Mapping
If you’re still a bit fuzzy on the tech speak, here’s a quick “cheat sheet” to help you master the conversation:
| Term | Simple Definition | Think of it like… |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping | The overall process of turning human text into a mathematical format. | Drawing a map where every word has its own GPS coordinate. |
| Tokenizzazione | Breaking a sentence into smaller chunks (words, prefixes, or characters). | Taking a Lego castle apart into individual bricks. |
| Embedding | A specific way of representing words as a list of numbers (vectors). | Assigning a “social ID number” to a word that describes its personality. |
| Vector | The mathematical name for the list of numbers that represents a word. | The exact latitude and longitude of a word on the AI’s map. |
| Attention | A mechanism that helps AI focus on which words in a sentence are most relevant to each other. | A spotlight that shines on the word “river” when it sees the word “bank.” |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing — the field of AI focused on human language. | The “English Department” of the Artificial Intelligence world. |
| Semantic | Relating to the meaning of words rather than just their spelling. | Understanding that “Home” and “House” are the same thing, even if they look different. |


![I 10 migliori siti web proxy di gioco per il 2026 [Guida definitiva]. i migliori siti web di proxy di gioco](https://www.okeyproxy.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/top-game-proxy-websites-500x333.jpg)




